China's officials will have clearer lines of command in the 'war on pollution', write Hu Tao and Lo Sze Ping

After
China's twin political sessions in March (known in China as
the 'Lianghui') central government put the finishing touches to a major
shake-up of the Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP), establishing separate departments for oversight of water, air and soil.
Think tanks and policy experts had long advocated
such a move, so that officials would have clearer responsibilities,
greater accountability, and defined lines of command.
The changes, which come one year after environmental
minister Chen Jining took up his post, are intended to improve the
quality of environmental management and avoid contradictory and muddled
decision-making within the MEP's manifold departments.
Marshalling China's officials more effectively, it is
hoped, could help win battles against chronic pollution and prevent
future environmental disasters.
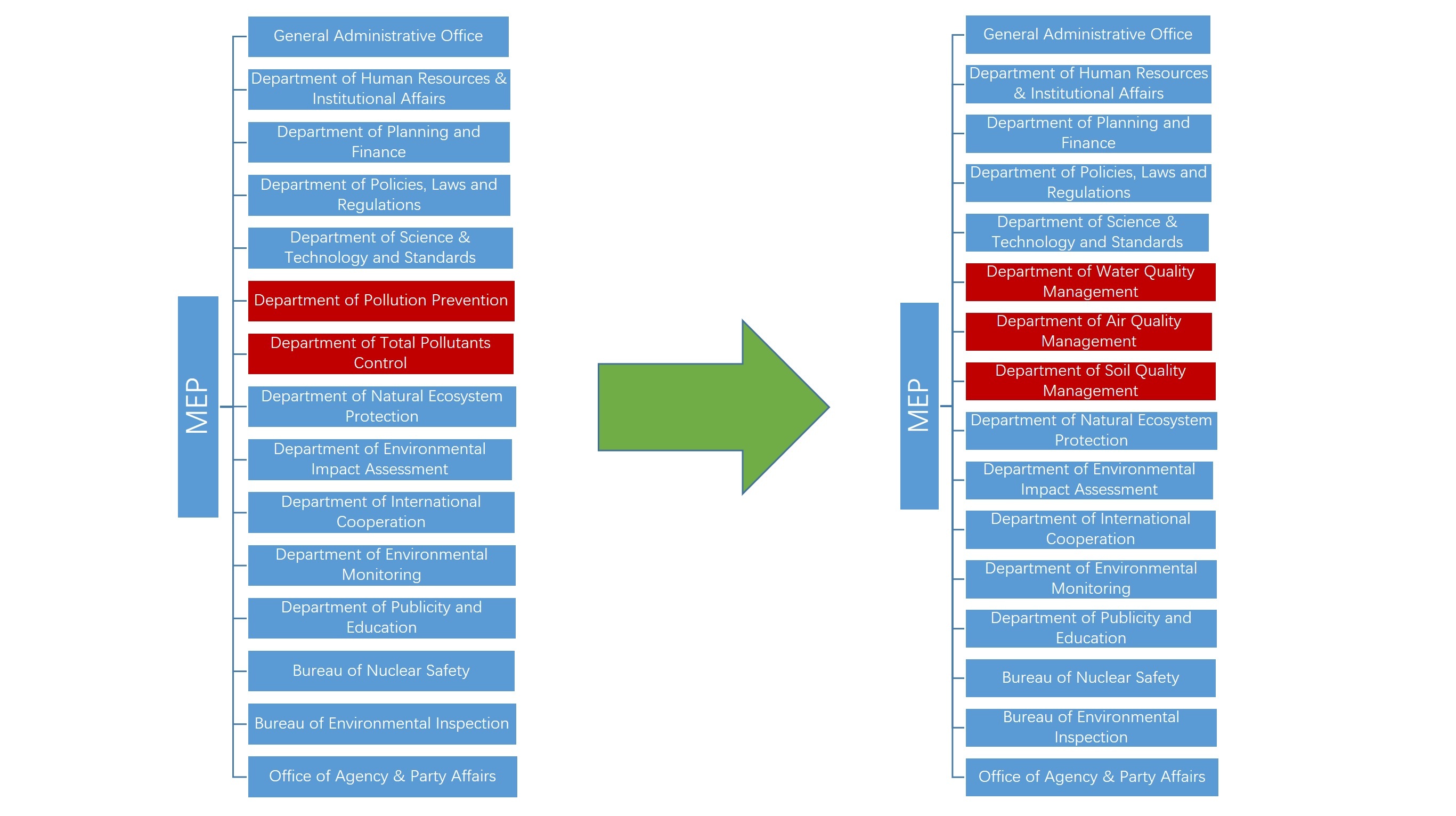
Proposed MEP “Three Departments Reform”
Air, water and soil
Previously, responsibility for air, water and soil was distributed across several departments within the MEP.

Proposed MEP “Three Departments Reform”
Air, water and soil
Previously, responsibility for air, water and soil was distributed across several departments within the MEP.
Management of water quality, for example, was spread
across the drinking water, catchments and oceans offices of the
Department of Pollution Control; and the water office and statistics
office of the Department of Total Pollutants Control. This amounted to
a bureaucratic mess that involved far too much overlap between the two
departments.
Meanwhile, environmental planning involved the Department of Planning and Finance; water legislation involved the Department of Policies, Laws and Regulations; and water standards involved the Department of Science, Technology and Standards.
Meanwhile, environmental planning involved the Department of Planning and Finance; water legislation involved the Department of Policies, Laws and Regulations; and water standards involved the Department of Science, Technology and Standards.
To further add to this tangle of red tape, oversight
of water standards involved two offices at the Department of
Environmental Monitoring, complicating efforts at consistent,
accountable decision-making.
That pattern of confusion and overlap within the MEP is repeated across ministries and commissions, and is true again for the management of air and water quality.
That pattern of confusion and overlap within the MEP is repeated across ministries and commissions, and is true again for the management of air and water quality.
The post-reform structure, based around specific
departments for air, soil and water, will better organise these
relationships. From now on implementation of laws or regulations (such
as the water pollution law or the air pollution action plan) will be the
specific responsibility of one department, with the support of other
departments.
Coordinated efforts
Some worry that dividing the environment ministry up in this highly-stratified manner will prevent it being seen as a coherent whole. Others worry about how to coordinate the different departments.
While air, water and soil sit under the environmental issue banner, they are also independent. And this reform changes how laws and regulations are drafted and implemented – but hasn't modified the environmental oversight of companies which have been largely responsible for China's multi-pronged environmental crisis.
Coordinated efforts
Some worry that dividing the environment ministry up in this highly-stratified manner will prevent it being seen as a coherent whole. Others worry about how to coordinate the different departments.
While air, water and soil sit under the environmental issue banner, they are also independent. And this reform changes how laws and regulations are drafted and implemented – but hasn't modified the environmental oversight of companies which have been largely responsible for China's multi-pronged environmental crisis.
Local environmental enforcement and inspection teams
are responsible for keeping tabs on polluting factories and power
plants, and these officials are unaffected by the most recent shake-up
in the MEP.
MEP reforms
We propose that reforms are continued throughout the environmental protection system, while other MEP departments are reduced in number, shrunk, or weakened.
The construction of a modern environmental management system requires should draw upon international experience in countries such as the US.
We propose that reforms are continued throughout the environmental protection system, while other MEP departments are reduced in number, shrunk, or weakened.
The construction of a modern environmental management system requires should draw upon international experience in countries such as the US.
In China, examples of powers that could be rolled
into the new departments include; setting standards (which currently
rests with the Department of Science, Technology and Standards); the
power to draft air, water and soil pollution laws (currently with the
Department of Policies, Laws and Regulations); and planning powers
(currently with the Department of Planning and Finance).
There is still much to be done in internal restructuring of the MEP and reform of environmental management systems. We hope Minister Chen Jining will continue this process, learn from international experience and fashion a new style of environmental management with Chinese characteristics.
There is still much to be done in internal restructuring of the MEP and reform of environmental management systems. We hope Minister Chen Jining will continue this process, learn from international experience and fashion a new style of environmental management with Chinese characteristics.
courtesy:chinadialogue
Comments